The Clean Air Act (CAA) is a US law aiming to protect public health by reducing air pollutants from industrial, power, and transportation sources via Select Emissions Regulations. These regulations include emission caps for factories, robust PRIM management, smart grid systems, strict automotive rules, and global warming restrictions. The CAA, led by the EPA, addresses various emissions sources, promotes green infrastructure, and collaborates with state agencies to enforce standards. While facing challenges like economic impacts and evolving science, Select Emissions Regulations are evolving to target specific health hazards, leverage digital monitoring, encourage voluntary reductions, and drive sustainable practices for cleaner air.
“Uncover the intricacies of the Clean Air Act, a landmark legislation striving for breathable, healthy air. This comprehensive guide navigates key aspects, from understanding the act’s foundational principles to exploring specific select emissions regulations targeting diverse pollutants. Delve into the impact of these regulations on industrial practices and environmental health. Additionally, we analyze challenges, controversies, and future trends shaping air quality regulation, offering insights into our ongoing quest for cleaner atmospheres.”
- Understanding the Clean Air Act: A Comprehensive Overview
- Key Objectives and Principles of Select Emissions Regulations
- Sources and Types of Emissions Covered Under the Act
- Implementing and Enforcing Clean Air Standards
- Challenges and Controversies in Emissions Control
- Future Trends and Innovations in Air Quality Regulation
Understanding the Clean Air Act: A Comprehensive Overview

The Clean Air Act (CAA) is a landmark environmental legislation in the United States, aiming to ensure safe and healthy air for all Americans. It sets national standards for airborne pollutants, providing a comprehensive framework to combat air pollution. The CAA’s primary goal is to protect public health and welfare by reducing various pollutants’ adverse effects on humans and the environment. This far-reaching act covers a wide range of topics, from setting limits on dangerous emissions to promoting research and monitoring strategies.
At its core, the Select Emissions Regulations under the CAA focus on controlling and reducing emissions from various sources, including industrial facilities, power plants, and vehicles. One key aspect is the implementation of greenhouse gas emission caps for factories, which aims to curb the release of potent heat-trapping gases contributing to climate change. Additionally, the act emphasizes the importance of Pollutant Release Inventory Management (PRIM) by requiring industries to track and report their emissions using advanced industrial emissions monitoring tools. These regulatory measures ensure transparency and accountability in air quality management, allowing for continuous improvements and a healthier environment for future generations.
Key Objectives and Principles of Select Emissions Regulations

The Select Emissions Regulations are designed to address specific environmental concerns, focusing on key objectives and principles that drive effective air quality management. These regulations aim to mitigate various forms of air pollution, with a particular emphasis on reducing harmful emissions from industrial processes, transportation, and energy production. The primary goal is to create a cleaner, healthier environment by implementing stringent standards that limit the release of pollutants into the atmosphere.
One notable aspect of these select emission management strategies is the integration of smart grid emission management systems. This innovative approach leverages technology to optimize energy distribution and reduce overall emissions. Additionally, the regulations enforce stringent automotive emissions rules, ensuring that vehicles meet specific pollution control criteria. By combining global warming emission restrictions with advanced air pollution control techniques, these policies strive to create a sustainable balance between economic development and environmental preservation.
Sources and Types of Emissions Covered Under the Act

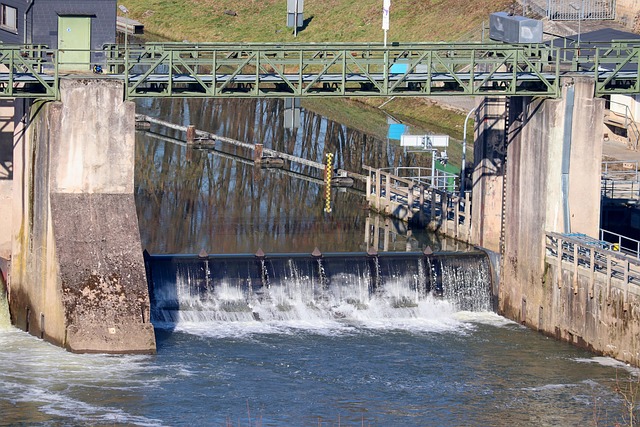
The Clean Air Act encompasses a wide range of sources and types of emissions to ensure clean air for all. These include emissions from industrial facilities, power plants, vehicles, and even biomass energy production. The select emissions regulations under this act are designed to mitigate various pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which have significant impacts on both public health and the environment.
In terms of specific coverage, international clean air legislation plays a crucial role in setting global vehicle emission norms, addressing transportation emissions control measures, and even considering biomass energy emission concerns. Alongside these, water pollution control measures are also integrated into the regulatory framework to ensure that efforts to improve air quality do not exacerbate other environmental issues.
Implementing and Enforcing Clean Air Standards
Implementing and enforcing Clean Air Act standards is a multifaceted process that involves various regulatory mechanisms and strategies. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a pivotal role in setting and monitoring these standards, ensuring compliance with select emissions regulations across different sectors. This includes transportation emissions control measures, which are crucial for reducing pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter from vehicles. Green infrastructure for air quality, such as urban forests and green roofs, is also gaining traction as a sustainable approach to mitigate local air pollution.
International clean air legislation further underscores the global commitment to addressing atmospheric contaminants. The EPA collaborates with state and local agencies to enforce these standards, utilizing tools like permits, monitoring, and enforcement actions. Electricity generation emissions are a significant focus area, with regulations targeting the reduction of sulfur dioxide and mercury from power plants. This comprehensive approach ensures that both domestic and international efforts contribute to the overall goal of maintaining and improving air quality for all.
Challenges and Controversies in Emissions Control
The Clean Air Act, while a cornerstone of environmental policy, faces ongoing challenges and controversies in emissions control. One of the primary hurdles is balancing the stringent reduction targets with the economic impact on industries. Select Emissions Regulations, aimed at curbing pollutants like nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, have sparked debates over their feasibility and cost-effectiveness. Industries argue that implementing these regulations, particularly greenhouse gas emission caps for factories, can lead to significant financial strains and job losses.
Moreover, the interpretation of air quality standards has been a point of contention. Regulatory agencies must navigate complex scientific data when setting limits, as seen in the case of industrial facility exhaust controls. The dynamic nature of technological advancements and changing environmental science makes it crucial for regulators to stay agile and adaptive, ensuring that emissions control measures are both effective and reasonable.
Future Trends and Innovations in Air Quality Regulation
As we move forward, the landscape of air quality regulation is poised for significant shifts and advancements. Future trends will likely see a greater emphasis on select emissions regulations, targeting specific pollutants known to pose severe health risks. This involves refining existing standards and implementing stringent automotive emissions rules to ensure vehicles contribute less to overall air pollution. The digital age plays a pivotal role here, enabling more accurate pollutant release inventory management through real-time data monitoring.
Innovations in regulation will also explore the potential of voluntary emissions reduction programs. By encouraging collaboration between industries and policymakers, these initiatives aim to foster sustainable practices that go beyond compliance. This approach not only addresses emerging pollutants but also promotes a more dynamic and responsive regulatory framework. The ultimate goal is to create a cleaner, healthier environment by leveraging technology and forward-thinking policy strategies.
The Clean Air Act serves as a cornerstone in the global effort to combat air pollution, with select emissions regulations playing a pivotal role in achieving cleaner air. By understanding the act’s key objectives, exploring covered emission sources, and addressing challenges, we can forge a path towards a healthier environment. As we look ahead, future trends in air quality regulation, coupled with technological innovations, hold great promise for continued improvements in air quality, ensuring a more sustainable and livable world.
